How to create an SEO strategy. Today’s digital era is one in which Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical element if you want to succeed online.
Whether a small business owner or a digital marketer for large corporations, a well-thought-out SEO strategy can generate more traffic to the website, enhance brand exposure, and eventually increase conversion rates.
However, formulating a comprehensive SEO strategy also requires a strategy. It is not something that can be thought about separately and pursued at random; rather, it usually encompasses several tactics that need to be integrated properly with the main direction of the business.
In this essay, we will go through the necessary processes for creating such a strategy, which will improve your website’s position in search engines and have the desired effects on the business.
Key Takeaways
- Set clear and measurable SEO goals that align with your business objectives.
- Regularly conduct SEO audits to identify areas for improvement.
- Perform thorough keyword research to understand and target user intent.
- Optimize both on-page and off-page elements to boost your SEO performance.
- Continuously track, analyze, and refine your SEO strategy for optimal results.
What is SEO?
SEO, an acronym for Search Engine Optimization, entails using strategies to increase a website’s position on Search Engine Results Pages for designated keywords. The principal initiative is to enhance the website’s visibility so that users can easily discover the content, thus increasing organic traffic.
How Search Engines Work
Google, Bing, and Yahoo are all search engines in one way or another. Every search engine has its own system for indexing and ranking the websites it covers.
Certain principles, such as the relevance of content, the structure of the website, and the adequacy of backlinks, have been used more often than not.
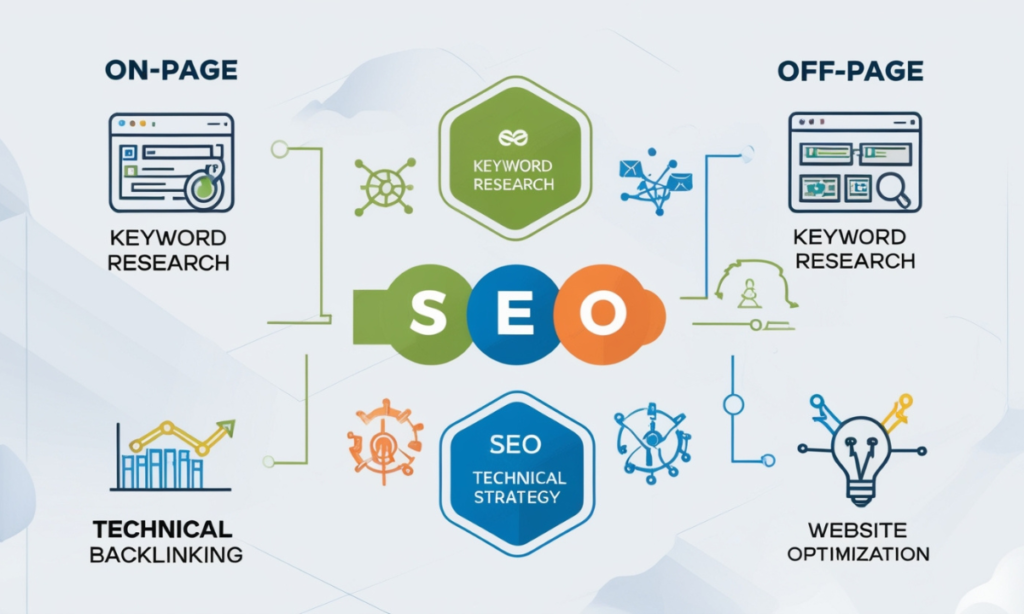
Key SEO Components
- On-page SEO is concerned with optimizing separate and individual pages on the website. It consists of keyword use, content, and HTML tags.
- Off-Page SEO: It is more about improving your site’s authority rather than the content or arranging sites on a page. It involves backlinks from other sites and presence in social networks.
- Technical SEO: Focused on improving core structural parameters of the website, including speed, mobile usability, and HTTPS.
Understanding SEO Goals
It is necessary to set clear boundaries and goals if you want to ensure that your SEO activity is in line with the general business goals we want it to achieve.
Setting SMART Goals
SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) help streamline targets regarding SEO. For example, an additional 20 percent organic traffic within six months or ranking in the first five positions for a chosen keyword within three months.
Aligning SEO Goals with Business Objectives
Your goals should work towards accomplishing the business’s general goals, such as brand equity, marketing leads, or sales.
Examples of SEO Goals and KPIs
| Goal | KPI | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Organic Traffic | Monthly Organic Visits | 20% increase |
| Improve SERP Rankings | Ranking Position | Top 3 |
| Boost Conversion Rate | Conversion Rate | 5% increase |
| Enhance Engagement | Bounce Rate | 10% decrease |
| Expand Brand Awareness | Social Shares | 15% increase |
Conducting an SEO Audit
An SEO audit is said to be an evaluation of the present SEO condition of a particular website. In this phase, you determine what should be improved to be able to do the necessary adjustments in your strategy.
Key Audit Components
- Content Audit: Inquires into what content is relevant and what content is situated.
- Technical Audit: This audit looks into site speed, mobile device accessibility, and indexes for crawling the site’s pages.
- Link Profile Audit: Investigates links pointing to your site, looking at the number and quality.
Tools for SEO Auditing
Google Analytics, Google Search Console, Ahrefs, and SEMrush are examples of popular SEO audit tools.
Keyword Research and Analysis
Advancement of search engine optimization begins with determining keywords. Keywords include words or phrases that seem to be widely used by potential customers, and the content of the website should be based on these keywords.
Steps in Keyword Research
- Brainstorming: The first stage of the process is to generate a list of relevant topics and words related to your business.
- Competitor Analysis: Research the worry sites and determine possible keywords.
- Tool-Based Research: Use this information, such as looking at the Keyword planner, Ahrefs, and SEMrush, to find search volume and keyword difficulty.
Keyword Research Tools Comparison
| Tool Name | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Google Keyword Planner | Search Volume, Keyword Ideas | Free |
| Ahrefs | Keyword Difficulty, SERP Analysis | $99+/month |
| SEMrush | Competitive Analysis, Rank Tracking | $119+/month |
| Moz Keyword Explorer | Keyword Suggestions, SERP Analysis | $99+/month |
| Ubersuggest | Keyword Ideas, Content Ideas | $29+/month |
On-Page SEO Strategies
On-page SEO entails adjusting the pages within your site with the aim of achieving better placement.
Content Optimization
Content design has to be highly accurate, content-rich, and tone-sensitive. This calls for naturally incorporating keywords into content that answers user intent and is beneficial.
Meta Tags and Headers
According to certain internet promotional scholars, title tags, meta tags, descriptions, and header tags (1,2,3) are crucial for the SEO process. Already, they serve a purpose and should consequently be targeted with important keywords regarding the structure of the content.
Image Optimization
Follow best practice, decrease the dimensions of the pictures, and add ALT tags that would make someone click on the pictures online. These measures improve both audience satisfaction and search engine optimization.
On-Page SEO Checklist
| Optimization Element | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Title Tag | Include primary keyword |
| Meta Description | Summarize content, use keywords |
| H1 Tag | Use once, include main keyword |
| ALT Text | Describe image, use keywords |
| URL Structure | Keep it short, include keywords |
Off-Page SEO Strategies
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your website to rank it higher in search engines.
Importance of Backlinks
Backlinks obtained from well-known websites add credibility to your website from the perspective of search engines. Extend your target to quality backlinks by guest posting, affiliate cooperation, or creating remarkable content.
Social Media’s Role
Social media signals are not pronounced ranking factors but may be helpful in boosting brand exposure and driving the audience to the website, which will help achieve the necessary impact for the SEO campaigns.
Technical SEO Strategies
This refers to the part of SEO that seeks to improve the structure of the site so that search engine spiders can easily access and index the pages.
Website Speed and Performance
Page speed is one of the most decisive factors in ranking a page. Page speed optimization requires the use of external applications such as Google PageSpeed Insights, which helps identify issues to address, such as optimizing images and cached browsers.
Mobile-Friendliness
Considering that mobile traffic contributes more than 50% of the worldwide web traffic, every website must be mobile-responsive. Provide a responsive layout suitable for all dimensions of the display.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
By providing structured data, search engines can better interpret your content, enabling rich snippets on pages and improving their SEO.
Technical SEO Essentials
| Technical Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Page Speed | Ensure fast loading times |
| Mobile Optimization | Implement responsive design |
| HTTPS | Use secure protocol |
| XML Sitemap | Submit to Google Search Console |
| Schema Markup | Add structured data for rich snippets |
Tracking and Measuring Success
Tracking your SEO activities is crucial for establishing what is effective and what needs improvement.
Key Metrics to Monitor
- Organic Traffic: Volume of visitors that come from search engines.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after only responding to one page.
- Conversion Rate: A certain percentage of visitors perform a certain required action.
- Backlink Profile: Sites that link back to your site regarding quality and quantity.
Tools for Measuring SEO Performance
SEO analytical tools like Google Analytics alongside Google Search Console are important in monitoring each SEO activity.
Other tools, such as Ahrefs and SEMRUSH, are complete, paid, and have additional features for other actions, such as rank checking and competition exploration through backlinks.
Creating Buyer Personas for SEO
Using ‘buyer personas’ aims to improve market targeting by improving SEO, as it captures set audience requirements and preferences.
Realizing who searches the Web for these topics and how such queries look can greatly improve the efficiency and relevance of your content marketing efforts.
Identifying Your Target Audience
Therefore the first step should be to seek information about the people you wish to serve. Consider the following:
- Demographics: age, gender, place of residence, level of income
- Psychographics: interests, values, challenges, etc.
- Behavioral Aspects: purchasing patterns, preferred means of communication, searching habits
Consider Google Analytics and social networks statistics in this case as well.
Mapping Content to Buyer Stages
There is no doubt that the customer decision stages may vary greatly. Focusing on the content for each of these stages allows reaching a wider audience. The most common are:
- Awareness: Customers start realizing that they have a problem. Therefore, content in this section should be focused on assisting users with more education, like blog posts or guides on reviews.
- Consideration: Customers are searching for ways to solve their problems. Content like comparisons, case studies, and reviews can yield good results.
- Decision: Customers have reached a point where they want to buy something. Product Sites and their offerings showcase, demos, and promos.
Using Buyer Personas to Inform SEO Tactics
It helps in getting the necessary keywords, tensions, and topics that are beneficial to the target audience. It also enables you to make content that focuses more on attracting and engaging the right audience and achieving optimum conversions.
Competitor SEO Analysis
Through competitor analysis, you can understand the success of your competitors in this area and determine what you should do to build your strategy accordingly. This method can find keyword gaps, backlink opportunities, and content niches.
Identifying Key Competitors
Investigate your industry and find out which businesses are your competitors by typing in words that are related to your business. Seek for:
- Main players provide the same range of goods or services.
- Secondary industry participants in similar processes or geographic markets.
Evaluating Competitor Keywords and Content
Ahrefs and SEMRush help you understand the keywords your competitors target and their content. The most important levers include:
- Top-performing keywords: Identify the keywords around which your competitors are riding high and try to find out what works for them.
- Content type and structure: Evaluate competitor content’s format, length, and quality.
Assessing Competitor Backlink Profiles
Backlinks from reputable sites boost credibility and rankings. Analyze competitor backlinks to identify:
- High-quality backlink sources: Look for reputable websites linking to competitors and consider strategies to secure similar backlinks.
- Broken links: Critique the style, size, and quality of the content produced by the competitors.
Advanced Technical SEO Techniques
Links from other websites, where content is published, are critical as they improve page authority and increase rank. Examining competitors’ backlinks can help:
Using Robots.txt and XML Sitemaps Efficiently
The robots.txt file guides search engine crawlers on which pages to index, while an XML sitemap lists all indexable pages, making it easier for crawlers to navigate your site. Ensure:
- Robots.Engage in a comprehensive link building search aimed at the high quality domains that have links to your competitors.
- XML Sitemap: Competitor websites have also been bound to include links that can be classified as broken. Utilize these links as they will give you a platform for your site content.
Leveraging Canonical Tags for Duplicate Content
Sometimes, having identical content in some elements on different pages lowers search engine ranking than expected. These tags include indicating the preferred canonical page for pages with similar or duplicate content on your website.
Improving Crawl Budget and Indexation
The crawl budget is the estimated number of pages that the search engine will be able to crawl within a specific time period on your site. Optimize your budget by;
- Eliminating or no-indexing low-quality pages (for instance, old or outdated pages).
- Eliminating dead ends or redirect loops will make it easier for crawlers to find and access more content.
Leveraging Social Media for SEO
Although social signals seem not to have a direct impact on rankings, incorporating social media in your strategies can go a long way in promoting your content indirectly by making your brand visible and driving traffic to it.
Social Sharing as an Indirect SEO Factor
The more widespread the content across various channels, the more backlinks and mentions it obtains since it is highly visible and appreciated by many users. Social channels can assist in creating awareness, which is more often than not turned into search visibility.
Influencer Partnerships for Content Amplification
This can help increase your reach significantly as influencers in your space can share your content. Influencers with profiled audiences can promote the content, create backlinks, and boost the authority of the brand.
Using Social Signals to Boost Visibility
Through frequent posting and interaction with Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other platforms, the audience can be built. The size and activity level of the audience determines how often others share, hit, and link to content posted on the site.
My Opinion
To formulate a well-working SEO plan, it is essential to know how the critical SEO features work – on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. To begin with, adopt SMART targets that align with business objectives and conduct an SEO audit.
Focusing on what your audience may be looking for and conducting a thorough keyword search to facilitate content creation I melting is most efficient while searching specific localities.
Successful off-page and on-page optimization should include creating high-quality links and web pages and improving technical optimization such as site speed, mobile optimization, and other structured data. Regular checking performance to find areas to adjust will allow for current SEO standards.